OpenGL ES 3차원 컴퓨터그래픽스 GL & Shader
ⓒ 2019. JungHyun Han Korea University Seoul, All rights reserved.
GPU Rendering Pipeline, All Transforms
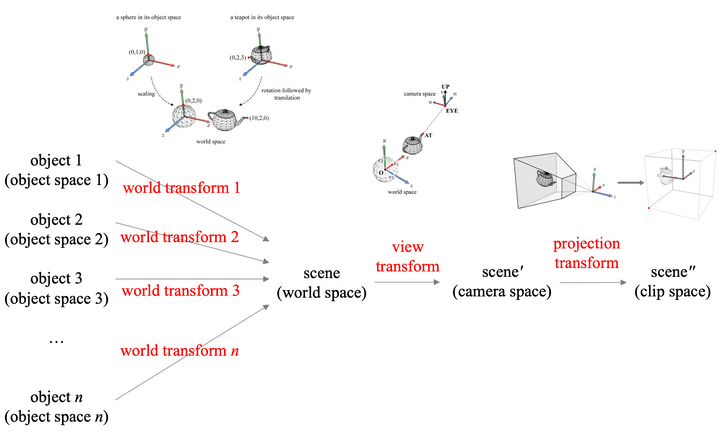
- 물체가 n개라면 n번의 world transform이 일어날 것이다.
Vertex and Index Arrays

-
texture coordinate라는 좌표도 vertex array에 각 셀에 같이 입력되는데, position, normal과 함께 필수 요소라고 볼 수 있다.
-
GPU는 parallel 프로세서이기 때문에 각 vertex들이 병렬적으로 처리될 수 있다.
OpenGL ES
Vertex Shader와 Fragment Shader는 결국 프로그램이기 때문에, 각자가 스스로 API에게 제공을 해야 시스템이 돌아간다.
- Shader를 짜기 위한 GPU에 특화된 언어를 사용해야하는데, 이를 OpenGL ES Shading Language라고 한다.(GLSL)
OpenGL ES Shading Language(GLSL)
GLSL은 C언어와 상당히 유사한 면이 있다. 하지만, GLSL은 GPU를 가동시키기 때문에, CPU를 가동시키는 언어들과는 차이가 있을 수 밖에 없다.
-
vec44차원 vector를 제공 -
ivec3정수형 3차원 vector 제공 -
mat3,mat4정사각 행렬 -
mat3x43x4 행렬
Vertex Shader
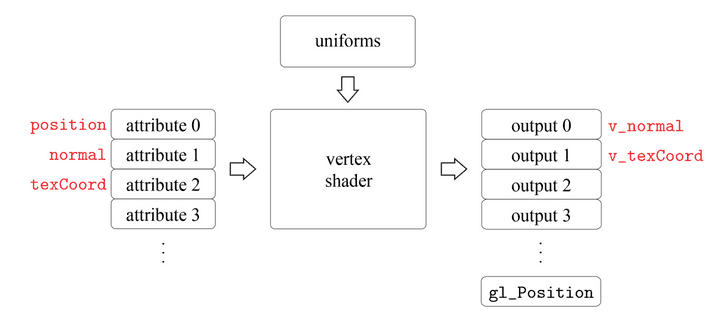
Two major inputs
-
Attributes : Vertex array를 구성하는 종류들 (ex, position, normal, texture coord) -> 각각의 vertex마다 다 attribute가 다르다.
-
Uniforms : 각각의 데이터들을 똑같이 적용해야하는 shader의 excution들을 칭한다. (ex, World transform, Projection, view transform)
클립공간에서 정의된 좌표를 출력하는 일은 vertex shader의 의무이다. 해당 좌표들을 bulit-in 변수에 저장한다.
#version 300 es
uniform mat4 worldMat, viewMat, projMat
layout(location = 0) in vec3 position;
layout(location = 1) in vec3 normal;
layout(location = 2) in vec2 texCoord;
out vec3 v_normal;
out vec2 v_texCoord;
void main(){
gl_Position = projMat * viewMat * worldMat * vec4(position, 1.0);
v_normal = normalize(transpose(inverse(mat3(worldMat))) * normal);
v_textcoord = textCoord;
}
-
3차원 좌표 position, 3차원 좌표 normal, 2차원 좌표 textCood를 attribute로 받는다.
-
in은 입력, out은 출력이다.
-
gl_position값을 얻기 위해서는 행렬 곱을 해야하는데, 선언된 position은 3x3 행렬인 Cartesian 좌표이고, 4x4행렬과 결합을 하기 위해서는 homogeneous coordinate로 바꿔줘야 한다.
-
vec4(position, 1.0)이라는 명령어를 통해 바꿔줄 수 있겠다. -
normal에 대해서는 우리가 배웠듯이
L파트가 필요한데, 이를mat3(worldMat)을 통해서 4x4행렬의 왼쪽 위 부분의 3x3부분을 뽑아낼 수 있다. -
inverse Transpose를 진행해야 v_normal이 나올 것이다.
GL Program(GL API)
- GL 명령어는 앞에 gl이 붙는다.
- GL 데이터 타입에는 앞에 GL이 붙는다.
Shader Object를 만들어야 하는데, glCreateShader라는 함수를 통해 만들 수 있다. 이는 glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER) 이런식으로 안에 argument를 넣어서 만들면 vertex shader과 fragment shader를 구분할 수 있게 된다.
GLuint shader = glCreatorShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
glShaderSource(shader, 1, &source, NULL);
glCompileShader(shader);-
GLuint = GL unsigned integer type
-
shader object에 실제로 shader코드를 저장하는 것
glShaderSource,&source를 통해 소스코드를 저장할 수 있다. -
glCompileShader를 통해 compile 할 수 있다.
Program Object
- vertex shader와 fragment shader가 만들어진 후에, 이 둘을 붙여서 program object라는 걸로 통합을 해야한다.
GLuint program = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(program, shader);
//glAttachShader(program, fragment_shader);
glLinkProgram(program);
glUseProgram(program);- 해당 프로그램에다가
vertex shaderobject를 붙여야 하기 때문에glAttachShader함수를 이용한다. - 연결해주기
glLinkProgram - 사용하기
glUseProgram
Attributes
Polygon Mesh의 데이터들을 .obj파일을 통해 vertex array와 index array를 import해올 것이다.
- 각각을 가리키는 pointer들을
vertices와indices로 설정해보자. - 각각을
objData라는 구조체에 모아져 있다고 해보자.
struct Vertex {
glm::vec3 pos; // position
glm::vec3 nor; // normal
glm::vec2 tex; // texture coordinates
};
typedef GLushort Index;
struct ObjData {
std::vector<Vertex> vertices;
std::vector<Index> indices;
};
Objdata objdata;glm는 OpenGL Mathematics를 의미하는데 유용한 유틸리티이다.
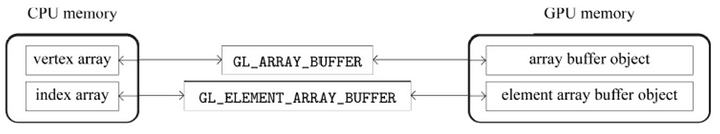
메모리에 vertex array랑 index array가 로드가 된 것인데, 이를 실제로 렌더링을 진행할 GPU로 옮겨주어야 하는데, 이를 GPU 메모리에 buffer object를 만든다고 표현한다.
- Vertex array → array buffer object
- Index array → element array buffer object
GLuint abo;
glGenBuffers(1, &abo);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, abo);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER,
(GLsizei) objData.vertices.size() * sizeof(Vertex),
objData.vertices.data(), GL_STATIC_DRAW);- Buffer를 생성해서 기존 vertex array를 연결해주고, 해당 데이터를 박아 넣는 느낌으로 이해하면 되겠다.
index array도 동일하게 진행된다.
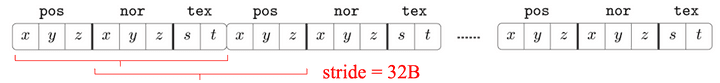
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0); // position = attribute 0
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
sizeof(Vertex), (const GLvoid*) offsetof(Vertex, pos));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1); // position = attribute 1
glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
sizeof(Vertex), (const GLvoid*) offsetof(Vertex, nor));
glEnableVertexAttribArray(2); // position = attribute 2
glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE,
sizeof(Vertex), (const GLvoid*) offsetof(Vertex, tex));-
시작점을 알려주는 것이 굉장히 중요해 보인다.
-
glEnableVertexAttribArrayVertex array 데이터를 활성화 시키겠다는 것이다. -
Vertex Shader에서 location 0, 1, 2에 position, normal, texCoord를 할당시켰던걸 기억해야한다.
-
3, GL_FLOAT→ 3차원 원소이면서, 각 원소는 float형태이다. -
sizeof(Vertex)= stride -
offsetof()→ 시작지점을 알려주는 함수
Uniform
Our vertex shader has three uniforms: worldMat, viewMat, and projMat.
- 매 씬마다 world matrix는 변동될 것이다.
- 카메라가 움직인다고 생각해봐도 view matrix는 계속 변동될 것임을 알 수 있다.
- projection matrix는 4가지 파라미터, fovy, aspect, n, f 이것들이 변하지 않은 이상 변화는 없을 것이다.
glm::mat4 worldMatrix; // repeatedly updated for a dynamic object
GLint loc = glGetUniformLocation(program, "worldMat");
glUniformMatrix4fv(loc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(worldMatrix));-
glGetUniformLocation프로그램 오브젝트 world 행렬의 위치를 찾아낼 수 있다. -
worldMat과worldMatrix는 다르다. worldMat은 shader가 갖고 있는 변수이고, worldMatrix는 openGL ES가 갖고 있는 변수가 되겠다. -
위치를 확인한 그 변수를 shader variable 자리에 넣어주면 된다.
Drawcalls
모든게 마무리 되면 이제 그리기만 하면 되겠다.
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 144);- index array없이도 이런식으로 호출이 가능하다.
glDrawElement(GL_TRIANGLES, 144, GL_UNSIGNED_SHORT, 0)
- element = 결국 index라는 점을 인지해야겠다.